Cold Flat Roof Insulation Thickness
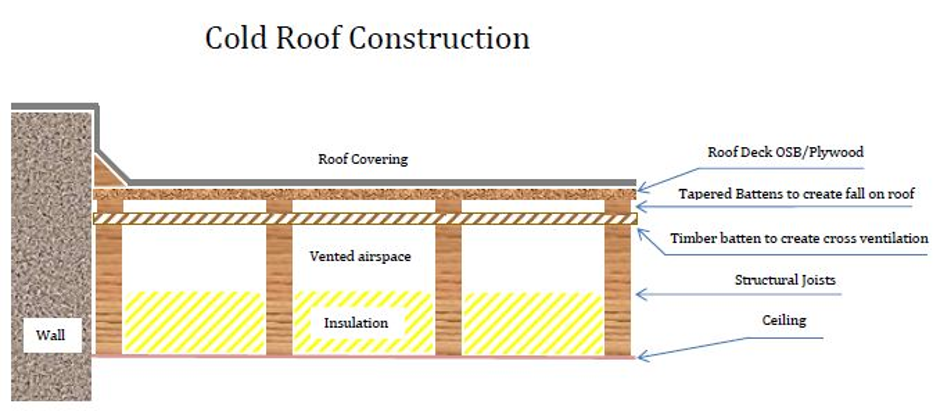
Lots of traditional flat roofs are of the cold roof construction type.
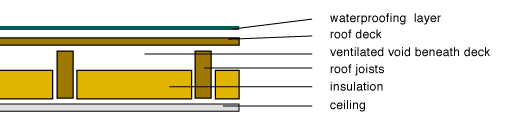
Cold flat roof insulation thickness. A cold roof has the insulation placed below the structural deck which thus remains cold. Cold roofs and warm roofs. Cold deck flat roof the thickness of insulation required will vary depending on the material you decide to use and the manufacturer s specification. It allows insulation to be added without having to replace the waterproofing on.
Refurbishing an existing timber joisted flat roof which has no insulation. There are two types of flat roof. A cold flat roof is one where the insulation is between or between and below the roof joists. Warm flat roof insulation.
Cold flat roof insulation. Saint gobain insulation uk manufacture and supply glass mineral wool slabs and rolls along with rigid polyisocyanurate pir boards that can be considered suitable for a wide range of applications across flat roofs whether you re looking to insulate at joist level or above the roof deck in your flat roof construction. There are two basic categories of roof design. This may help with condensation but causes such a loss of heat that it has been banned in scotland.
Cold deck this is where the insulation is placed between the joists rafters or in between the ceiling joists in the case of a pitch roof. This means there is a vapour control layer in the ceiling and cross ventilation at the eaves or the top of the walls. Ventilation openings either at. Warm deck the type of insulation for this is usually of a rigid type and the thickness will vary depending on the manufacturer s specifications.
Alternatively battens can be secured to the underside of the. Many properties use this option as there are no additional costs for scaffolding or organising how to gain safe access to the roof exterior. Ventilation is required for these roofs. A warm roof has the insulation above the structural deck which is thus kept warm.
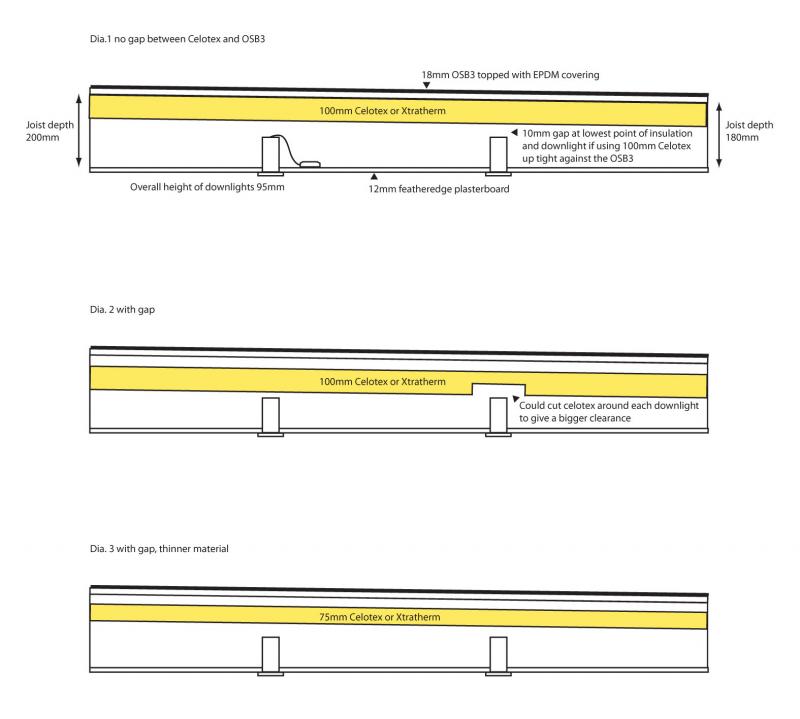
With a flat roof this issue does not arise but the u value constraint and the amount of insulation needed is just the same. In this case ventilation is required and the roof can still become wet with condensation which may cause materials to decay. Achieving a u value of 0 20w m meaning your roof will be better insulated than your walls will need 120mm thickness of rigid foam or 200mm of mineral wool or natural insulation. The insulation is below the deck but above the plasterboard.
A ventilation gap usually 50mm should be provided between the top of the insulation and underside of the roof covering to allow the air to flow across. The waterproof layer is above the insulation and a vapour control layer is placed below the insulation. The insulation material is placed between the supporting joists leaving a gap of 50 60mm between the roof and insulation.